The healthcare industry has been at the forefront of many advancements, and the use of technology has made its innovation particularly notable. With progressive disruptions, rapid adoption of telehealth, mHealth apps, online consultations, and AI in healthcare, privacy and security risks have also crept in. AI-driven healthcare is also transforming the way the healthcare segment detects Fraud, Waste, and Abuse (FWA) and identifies early spending patterns.
Malicious actors are seeking to exploit patient-related data available online. This is one of the many new reasons that compliance focuses on resolving in the healthcare segment. This blog aims to delve into the steps you can take to build a healthcare app or software while staying compliant with healthcare standards.
If you’re looking to build a healthcare-compliant app or software, you need to learn more about healthcare compliance standards and ensure your healthcare solution is compliant. Let’s take a quick tour of what this healthcare compliance guide can cater to your business or organization.
TL;DR Healthcare compliance means following laws, standards, and internal policies to protect PHI, reduce fraud, and keep patients safe. Non-compliance can cause data breaches, fines, legal action, license risks, and reputational damage. Between 2009 and 2024, OCR reported 6,759+ breaches of 500+ records in healthcare. A strong compliance program is built on risk assessments, staff training, clear policies & procedures, internal audits, and structured incident management. Key regulations like HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR, FDA, FD&C, FTC rules, and Stark/Anti-Kickback define strict requirements for privacy, security, breach notifications, fair referrals, marketing, tiered penalties that can cost you millions. Organizations must continually monitor, document, and improve via audits, data security reviews, breach response plans, vendor due diligence, BYOD policies, and adherence to a detailed compliance audit checklist. AI reshapes compliance by automating checks, monitoring EHR access, spotting billing or credentialing anomalies, improving documentation accuracy, and flagging real-time risks in “smart hospital” environments. Partnering with a healthcare app development company helps you build mHealth, telehealth, and AI-driven healthcare apps architected for compliance by design—aligning your software, processes, and governance with global healthcare standards. |
Moving further, there is a shift from reactive strategies to a proactive approach. This change focuses on learning potential legal and regulatory concerns before escalation strikes. Presently, healthcare organizations are actively contributing to innovation, finding areas for improvement, and following healthcare standards. Before learning more about healthcare compliance best practices, let’s understand what healthcare compliance is and why you need healthcare compliance for your organization or business.
What is Healthcare Compliance?
The term is broader than it looks, because healthcare compliance involves the collective efforts of medical organizations and businesses to implement reliable security measures, protocols, and procedures. This is necessary to prevent abuse, fraud, and misuse of healthcare-specific data, assets, or anything related to the business. Adopting secure, standard procedures helps organizations meet the ethical, professional, and legal standards set by various healthcare laws.
For example, once a medical association deploys stringent data privacy measures to store, secure, and share the patient’s medical-related information, it indicates that the organization follows laws, regulations, guidelines, and compliance pertaining to the industry.
There are many federal, state, local, and private agencies that are responsible for issuing healthcare compliance regulations. Healthcare compliance laws are complex and can change continuously due to workflow concerns, internal audits, ongoing advancements, IT compliance modifications, etc. Not complying with healthcare regulations can result in legal penalties, including federal fines.
This is why healthcare firms have team members dedicated to particularly emphasizing regulatory compliance. Ensuring compliance in the healthcare sector requires strong collaboration among legal professionals, software development companies, and compliance officers.
Defining the Purpose of Compliance in Healthcare
Healthcare compliance encompasses a wide range of practices across both small and large medical institutions. With this holistic approach, regulatory compliance in healthcare involves risk management, healthcare governance, and GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance), all of which are required to build a secure, high-performing environment.
The core purpose of urging medical associations to comply with GRC standards is to enhance patient care. But most healthcare compliance and regulations also emphasize patient security, data privacy, medical billing, and related data.
To be precise, healthcare compliance is important because:
- The healthcare industry is huge, and the sensitivity of the services it offers leaves it open to potential risks. This is due to data moving through multiple hands, which creates significant compliance issues.
- Healthcare services directly impact human lives, which makes it essential to maintain integrity standards to ensure patient safety.
- Keeping up the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of Protected Health Information (PHI) is significant for safeguarding patients’ trust, rights, and privacy.
- Compliance minimizes fraud and helps ensure funds are used appropriately.
- Data breaches can cost organizations money, disrupt business continuity, damage brand image, and destroy customer relationships.
- Compliance programs proactively identify vulnerabilities and help eliminate or reduce the impact of incidents.
- Compliance fosters trust among clients and stakeholders and introduces great business opportunities.
Real-Time Examples for Biggest Healthcare Data Breaches: Why You Need to Stay Healthcare-Compliant?
1. Episource
Occurred in 2025.
What Happened: A cybercriminal attacked Episource’s system and stole data, affecting 5.4 million people. The service provider’s inadequate protection of its systems caused this exposure.
Takeaway: Even third-party service providers that embrace healthcare entities are at high risk. Following robust monitoring and vendor security is essential.
2. UnitedHealth Group
Occurred in 2024 and continued to 2025.
What Happened: The attack impacted core healthcare-technology operations and exposed massive personal and health-insurance data of 190 million people.
Takeaway: Large centralized tech platforms are severe targets. A weak link in the service provider or supply chain can negatively impact thousands of patients and healthcare providers.
3. Aspire Rural Health Systems
Occurred in 2024-2025.
What Happened: About 138,000 users’ data, including HR/Financial documents, patient records, and insurance information, have been exposed due to unauthorized access to internal systems by a ransomware group.
Takeaway: Smaller networks and rural systems are also at high risk; cyber threats are not restricted to large hospitals.
✅ Why is having a compliant app/software so important?
- Compliance forces you to include encryption, security, privacy, and access controls in the design before problems occur, preventing major breaches.
- While an application or system is built with regulatory compliance standards in mind, you minimize legal/financial risk, secure your brand integrity, and foster patient trust.
- Healthcare-related information is highly sensitive, and breaches can cause business disruption, patient harm, and regulatory fines. Compliance is not optional; it is essential.
A Quick Look At the Key Healthcare Compliance Statistics
- The global healthcare compliance software market value is projected to reach 6503.3 million USD by 2030.
- Between 2009 to 2024, OCR reported 6759 healthcare data breaches of 500 or more records.
- 88% of hackers attack healthcare entities for financial reasons.
- Malware attacks and IT-related incidents accounted for 67% of data breaches in the healthcare segment, and tally for 92% of all breached medical records.
Evolution of Healthcare Compliance in the USA
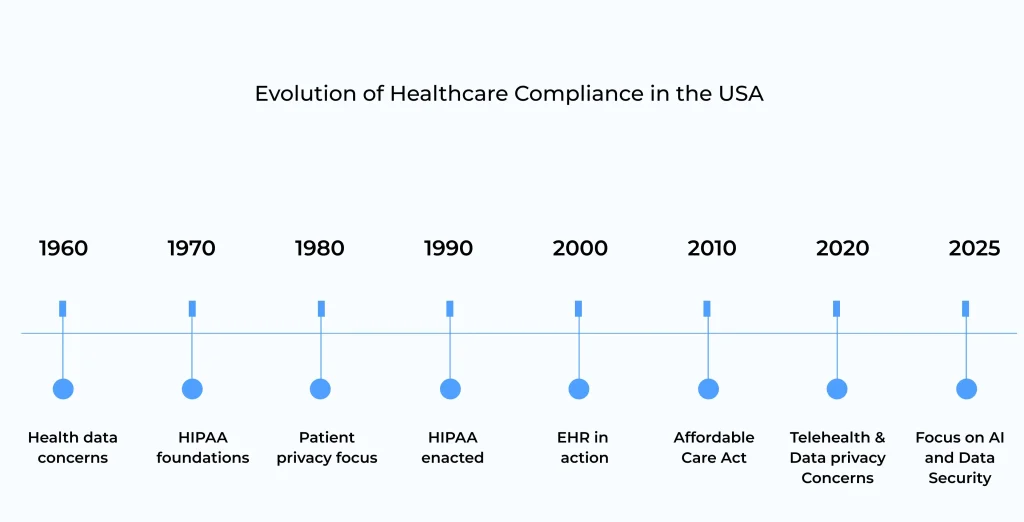
1960s: Initial conversations started about privacy and the security of patient health data.
1970s: HIPAA foundations began to form, focusing on future healthcare data regulations.
1980s: Improved focus on patient privacy-growing concerns, and conversations about patient data protection.
1990s: Implemented the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), focusing on data privacy and security.
2000s: Introduced Electronic Health Records (EHR), focusing on improving patient data access and management.
2010s: The Affordable Care Act was introduced, strengthening healthcare rules, including data privacy provisions.
2020s: Rapid growth of telehealth that raised new challenges in healthcare compliance, especially in data security and privacy.
2025s: With AI and Machine Learning playing a massive role in healthcare, regulations evolve to boost data protection, compliance, and ethical use of AI in the patient caregiving process.
Core Elements of Healthcare Compliance
When dealing with healthcare compliance, you need to consider five core elements that outline the processes for creating cultural compliance within your organization. These elements lay the foundation for risk mitigation and regulatory adherence.
- Healthcare Risk Assessment
This isn’t a usual compliance exercise in which one finds risks and resolves them. It identifies potential concerns that can impact patient care, safety, or regular operations. The objective is to understand what could go wrong, evaluate the likelihood and complexity of the risks, and follow steps to alleviate or reduce them.
With risk assessments, organizations might have these questions in mind:
- What is the adequacy of the current measures?
- What annexations are still possible?
- Are all operational procedures, including process flows to third-party vendors, analyzed to eliminate risk before it poses a threat?
It becomes risky when new layers are added, such as cloud-based software management and contractor interaction. Ad hoc risk assessment processes can point to vulnerabilities that leave an organization blind to real risks.

- Employee Training Program
With healthcare training, you can equip employees with the skills and confidence to respond to any situation. You need to ensure your employees are prepared to address challenges in infection control, patient care, and compliance audits.
This is why a great training program is needed:
- When employees are well-trained in the recommendations, patients can receive excellent care at the healthcare facility.
- Good training can discharge your organization’s liability limit and help alleviate legal concerns.
- Once learning is standardized, it leads to minimal errors, less repetition, and more skilled employees in the organization.
- Everyone receives training and knows what to do for a particular task.
- When employees are informed, assured, and can deliver.
- Policies and Procedures
In healthcare cybersecurity, policies and procedures are protocols that define a specific course of action for managing and protecting information. Creating such policies and ensuring they remain true to existing practices can seem challenging. Healthcare organizations should keep the policies relevant, active, and compliant, which demands continuous vigilance.
Now, here are the policies that should be the key components of every healthcare cybersecurity strategy.
- Data encryption policy
- Access control policy
- Password management policy
- Incident response policy
- Employee training and awareness policy
- Remote access policy
- Data backup and recovery policy
- Third-party vendor management policy
- Privacy and confidentiality policy
- Audit and monitoring policy
- Internal Audits Over Regulatory Audits
Internal audits are necessary while managing compliance concerns in healthcare facilities. The primary purpose of such audits is to determine whether healthcare providers comply with applicable laws and regulations. Hence, it is essential to understand that while external audits can occur at any time, internal audits give the company time to anticipate and prepare for the process.
Generally, few regulatory bodies offer 7-60 days’ notice, while internal audits support high-risk management and problem-solving. Documentation is extremely essential, because when it is not in writing, it is assumed it never occurred. Partnering with a software or app development company that builds healthcare software in adherence to applicable policies is necessary to ensure your solutions remain compliant.
- Incident Management
This structured process can detect, assess, and eradicate organizational hazards. It is specifically designated to resolve existing incidents and eliminate recurrence through in-depth analysis and corrective procedures. Core threats that should be addressed and managed are:
- HIPAA Violations: Situations where patients’ privacy rights or health information security are violated.
- Cybersecurity Attacks: Cyber threats, attacks, and malware are compromising information technology assets.
- Physical Hazards: These can cause trips, slips, and falls, resulting in injuries.
- Accidental Roadblocks: Hazards created by improper utilization of sharps.
- Chemical Exposure: While in contact with hazardous materials, exposure occurs.
- Theft and Loss: Damage, loss, or trespass to or destruction of data or physical assets.
- Workplace Violence: Regardless of the inviolable state of the place, violence is carried out in healthcare facilities.
- Natural Disasters: Situations where ongoing business activities are affected by events such as floods, fires, and earthquakes.
- Human-Made Error: Methods that personnel can take and create undesired conditions or consequences to the organization.
- Network & Technological Failures: Disruptions to the conventional operational process, information access, or communication.
Who Regulates Healthcare Compliance?
Agencies at the Federal and State levels regulate healthcare compliance. The key regulators are as follows:
- Department of Health & Human Services (HHS): Regulates healthcare programs and regulations like HIPAA.
- Office for Civil Rights (OCR): Ensures HIPAA enforcement to maintain patient data security and privacy.
- Office of Inspector General (OIG): Oversees any abuse, fraud, and misuse in healthcare programs with HHS
- The Joint Commission (TJC): Certifies and acknowledges US healthcare organizations.
- Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): Offers programs to work in quality initiatives.
- Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA): Follows controlled substances regulations.
- Food & Drug Administration: Follows the safety and security of drugs, food supply, and medical devices.
Different Healthcare Compliance Standards
Digital health compliance has detailed structures that list the must-haves and drawbacks for Health Information Technology (HIT), wearable technology, custom prescriptions, and telehealth. Healthcare mobile applications are the most modern way of delivering medical services, particularly during and after the pandemic. Here are the compliances in healthcare that organizations should adhere to:
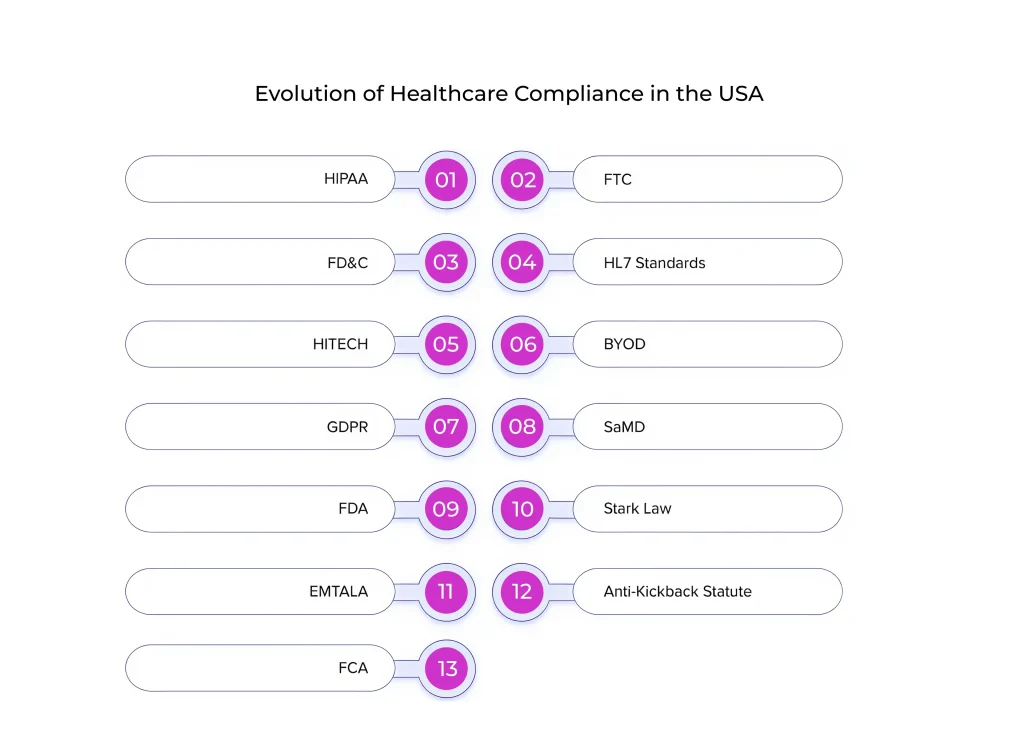
HIPAA
Enacted by the OCR, i.e, Office of Civil Rights, the act is enforced within the US Department of Health & Human Services. HIPAA (Healthcare Insurance Portability & Accountability Act) protects the privacy and security of eligible health information and, in certain cases, helps prevent data breaches. Failing to comply with HIPAA can cause penalties of up to 50,000 USD for every violation, depending on the extent of the violation.
To save you from paying off such huge penalties, you can rely on a HIPAA-compliant healthcare mobile app development company to build apps that protect sensitive medical information pertaining to hospitals, doctors, and patients.
What are the HIPAA violation penalties?
| Level | Condition | Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | Lack of knowledge about HIPAA violations and the failure to adopt reasonable due diligence wouldn’t have led to HIPAA violations. | $100- $50,000 per violation (maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million) |
| Tier 2 | Reasonable cause that the entity covered learnt about or would have learnt about the violation by adhering to the reasonable due diligence. | $1000- $50,000 per violation (maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million) |
| Tier 3 | Willfully neglecting HIPAA rules with violations corrected within 30 days of discovery. | $1000- $50,000 per violation (maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million) |
| Tier 4 | Willfully neglecting HIPAA rules and not trying to correct the violation within 30 days of discovery. | $50,000 per violation (maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million) |
FTA
The FTC (Federal Trade Commission Act) includes regulatory protocols that address unfair or deceptive claims, data privacy, data security, business malpractice, and other specific challenges. The act defines unfounded claims regarding the use of mHealth apps. Under the Health Breach Notification Rule, healthcare IT consulting companies must report breaches involving personal health records.
What are the FTA violation penalties?
| Violation Type | Penalty (Per Violation) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Unfair practices under the FTC Act | Up to $50,120 – $53,088* | Adjusted yearly for inflation |
| Violation of a final FTC cease-and-desist order | Up to $10,000 (statutory) | May vary based on inflation |
| Violations under the FTC’s Penalty Offense Authority (repeated or known violations) | Up to $50,120 – $53,088* | Per violation, according to the affected consumer |
| Non-compliance with the Health Breach Notification Rule (for non-HIPAA apps/platforms) | Up to $53,088* | Can apply to digital health apps, telemedicine platforms, etc. |
| Large-scale deceptive healthcare advertising or privacy breach (settlement cases) | Typically $1M – $7M+ (case-based) | Eg, Cerebral ($7.1M), Evoke Wellness ($7M) |
Note: *Penalty amounts vary based on annual inflation adjustment (per 16 CFR §1.98).
FD&C
Better known as FD&C, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act ensures that medical devices and apps meet established standards and are safe for public use. Also, not all healthcare applications fall under this jurisdiction, but those that can’t deliver on their claims and have critical consequences for consumer health are subject to the FD&C Act.
What are the FD&C violation penalties?
| Violation Type | Penalty (Per Violation) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| General FD&C Act violations (adulterated/misbranded drugs, devices) | $1,000 to $1,000,000+ | Amount varies based on severity and intent |
| Drug/medical device safety reporting violations | Up to $250,000 (individual) or $1,000,000 per proceeding | Applies to violations of Sections 355(o), 355(p), etc. |
| False or missing drug sample reporting | Up to $100,000 | Applicable to sample distribution violations |
| Tobacco product violations (if applicable) | $15,000 – $250,000 per violation | Cumulative fines can reach $10M |
| ClinicalTrials.gov reporting failures | FDA may impose civil penalties (amount varies) | as required under FDA regulations |
HL7 Standards
HL7 (Health Level Seven International) is a non-profit organization responsible for creating standards for exchanging, integrating, sharing, and retrieving e-health information to support procedural health practice. A great healthcare app development company follows a set of global standards for the use of healthcare data, as stipulated by HL7.
| 💡While non-compliance with HL7 standards doesn’t cause fines, it can end up in lost contracts, integration issues, and regulatory risks if weak data exchange causes patient impact or data exposure. |
HITECH Act
HITECH (Healthcare Information Technology for Economic & Clinical Health) was implemented in 2009. The act focuses on promoting enterprise adoption of Health Information Technology using EHR (Electronic Health Records). mHealth apps have embraced this practice, and it is important to abide by the rule while also ensuring strict enforcement of HIPAA security and privacy rules.
What are the HITECH Act violation penalties?
| Violation Type | Penalty (Per Violation) | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Failure to inform affected users of a breach | Up to $50,000 | Notification within 60 days |
| Failure to notify HHS (if >500 individuals affected) | $50,000 | Mandatory reporting |
| Failure to notify media (for large breaches) | $50,000 | If >500 are affected in a region |
| Improper use/disclosure of PHI | $100 – $50,000 | Based on HIPAA penalty tiers |
| Willful neglect not corrected | $50,000 | Can reach $1.5M/year |
| Breach due to inadequate safeguards (e.g., no encryption) | Up to $1.5M annually | Encourages encryption |
| Intentional misuse or sale of PHI | Criminal penalties | Fines + possible jail |
BYOD
This practice enables healthcare organizations to allow medical staff to bring smartphones and tablets into offices. However, when mHealth solutions are not custom-tailored to your BYOD security protocols, things can get scary. Think of a situation in which an employee loses a smartphone or device that has access to PHI (Protected Health Information). In this case, you need a mobile device management strategy in place. While developers develop an mHealth solution with features like remote wipe, you can simply delete all the data linked to the lost device, such as emails and browser history. Considering such processes during the initial SDLC stages can help companies procure BYOD approval.
GDPR
Better known as GDPR, the General Data Protection Regulation applies to smartphone apps that collect and process the personal data of European Union citizens. Privacy protection is a major driver of the GDPR, and the federal authorities have made efforts to hand over some control over personal data to the layman. It also keeps business processes related to private data management out in the open.
What are the GDPR violation penalties?
| Severity Level | Maximum Penalty | Whichever Is Higher | Healthcare Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower-Tier Violations (e.g., failure to appoint a DPO, poor record-keeping) | Up to €10 million | Or 2% of global annual turnover | Applicable, but rarely used for health data violations |
| Higher-Tier Violations (e.g., unlawful processing, insufficient safeguards for health data, data breaches) | Up to €20 million | Or 4% of global annual turnover | Most healthcare violations fall under this category due to the sensitive nature of medical data |
GDPR best practices in healthcare to follow:
- Gather explicit consent to process healthcare data.
- Use only necessary data to follow the data minimization principle.
- Execute Privacy by Design & Default in all healthcare apps and systems.
- Encrypt health data at rest and in transit, using pseudonymization whenever possible.
- Implement role-based access control and leverage secure authentication.
- Ensure GDPR rights, make sure patients can access, correct, delete, or port the data.
- Communicate data breaches to the supervisory authority within 72 hours.
- Inform the impacted users if the breach poses a high privacy risk.
- Implement a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) before launching risk-oriented health systems (EHRs, AI apps, telehealth).
- Ensure legal and secure cross-border data transfer with approved mechanisms.
- Offer regular staff training on data protection, breach handling, and phishing.
- Make sure all third-party vendors are GDPR-compliant and have a Data Processing Agreement (DPA).
- Maintain detailed records of all data processing activities.
- Define and adhere to data retention and secure deletion policies.
- Arrange a Data Protection Officer (DPO) in case of processing health data at scale.
- Leverage strong logging and auditing to track access to patient-specific data.
- Stop using health data for secondary purposes, such as marketing, without additional consent.
- Regularly perform vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
SaMD
The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), the global alliance advocating systematic regulation of medical devices, devised Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) to provide real-time guidance to support the evolution of digital technologies in this niche. Headed by the FDA, the association has deployed a series of frameworks to consider risk classification, clinical assessment, and quality management systems.
FDA
As a core component of the US Department of Health & Human Services, the FDA (Food & Drug Administration) regulates the development, manufacturing, safety, effectiveness, and marketing of medical devices, pharmaceutical products, and biologics.FDA compliance is necessary to ensure patient safety and product quality.
What are the FDA violation penalties?
| Violation Type | Penalty |
|---|---|
| Failure to comply with clinical trial registration or results submission | Up to $10,000 / proceeding |
| Continued non-compliance after 30-day notification (clinical trials) | An additional $10,000 per day |
| Failure to report drug sample distribution | Up to $100,000 per violation |
| General FDA healthcare regulatory non-compliance (e.g., safety violations) | Typically $10,000 – $20,000 per violation |
| Serious violations involving fraud, concealment, or patient harm | May lead to multi-million dollar settlements and/or criminal charges |
Note: Penalties vary based on severity, intent, duration, and the patients or devices affected.
Stark Law
The rule restricts physicians from referring patients to receive dedicated health services, usually payable by Medicaid or Medicare, from the organization with which the physician or their immediate family members share a financial relationship. The rule focuses on preventing physicians from self-dealing while ensuring legitimate healthcare arrangements.
EMTALA
EMTALA (Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act) requires hospitals to offer emergency care to anyone, without considering their ability to pay or insurance status. The rule avoids patient dumping while ensuring everyone has access to emergency treatment.
Anti-Kickback Statute
The rule prohibits the exchange of remuneration, such as bribes or kickbacks, for services or patient referrals covered by Medicare and Medicaid. The law focuses on preventing financial gain from influencing healthcare treatment decisions.
False Claims Act
The act makes it a crime to file a false claim for a federal program. Under FCA, private individuals can file lawsuits on behalf of respective governments, providing financial incentives for exposing fraudulent activities. If a healthcare provider knowingly makes false claims or hides the truth, they are subject to pay up to $27,894 per claim, including triple damages, and, in extreme cases, may also face criminal prosecution.

Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance in healthcare can lead to serious legal and financial consequences. This can impact the organization’s reputation and stability. Let’s look at the key consequences:
- Fines: Regulatory bodies such as OCR can impose penalties of almost thousands to millions of dollars.
- Settlement Costs: Lawsuits related to non-compliance can drain resources and increase costs.
- Loss of Funding: This can lead to service cuts, layoffs, and closures.
- Legal Consequences: Civil lawsuits, criminal charges, and license revocation can result in long-term reputational and financial losses.
Strategies to Prevent Non-Compliance: Key Steps You Should Follow
Healthcare professionals can win the trust of the public and prevent legal problems through the following steps:
- Compliance rules are continually evolving and are increasingly complex. Organizations should be educated and able to address these dynamic needs with advanced knowledge.
- Ongoing training of the entire staff needs to be prioritized and regularized. Improving scrutiny at every step is an ideal way to never violate compliance.
- Make sure you maintain open communication with the compliance officer to implement continuous improvement, ensure compliance, and maintain legal requirements during risk identification.
- Keeping focus on privacy and information security with encryption can help prevent breaches. This can be implemented by limiting access to health apps and information, preventing connected-device risks, and conducting regular risk assessments.
A futuristic healthcare software is the most intelligent way to ensure compliance. By following a well-laid healthcare app development process aligned with industry standards, you can stay compliant.
How Much Does Healthcare Compliance Cost?
Across industries, organizations continue to face evolving compliance needs and data privacy regulations. The cost to attain compliance has rapidly increased in a few heavily regulated industries, such as healthcare. While ensuring regulatory compliance can be costly and complex, the alternative is likely more expensive, with significant fines and heavy tolls, including customer trust, legal fees, remediation, and more.
| Compliance | Costs Involved |
|---|---|
| HIPAA | $25,000 – $1,20,000 |
| HITECH Act | Included in HIPAA, but usually adds $10,000-$50,000 more |
| GDPR | $50,000-$2,50,000 |
| HL7 Standards | $20,000 – $100,000 |
| SOC 2 | $20,000-$80,000 |
| ISO 27001 | $20,000-$75,000 |
| Stark Law & Anti-Kickback Statute | $10,000-$60,000 |
| CCPA | $15,000-$100,000 |
| FDA | $70-$500 |
| ONC Certification | $20,000- $150,000 |

Introducing AI in Healthcare Compliance
As per Research and Markets, ‘smart hospitals’have taken a new rise through the adoption of digital tools such as data management systems, Internet of Things, AI, and robotics, witnessing exponential growth. The smart hospital market grew from $57.5 billion in 2023 to $67.6 billion in 2024. By 2030, it is anticipated to hit $187 billion.
By automating compliance checks, tracking updates, and verifying provider credentials, AI helps the healthcare team gain an edge in regulatory compliance. Likewise, the technology minimizes the risk of human errors, which can lead to administrative burdens or inefficiencies.
- Automation of Compliance Checks
Compliance audits usually involve extensive paperwork, manual data entry, and revisions to multiple regulatory processes. AI is a time-saver here with automated processes that streamline all these tasks. It helps with:
- Reviewing records
- Tracking provider credentials
- Detecting inconsistencies
- Identifying possible compliance violations
For example, AI-specific healthcare credentialing systems can quickly verify whether a provider’s licence is active and compliant with existing regulations. This eliminates unintentional lapses that could lead to fines or reputational penalties.
- Enhancement of Data Accuracy & Reporting
Keeping detailed records is necessary for regulatory compliance; however, even minor documentation issues can negatively impact patient care, such as missing provider details. With AI, organizations can improve data accuracy, automatically check records in real time, and identify discrepancies such as billing code errors before they become major compliance problems.
- Real-Time Identification of Compliance Risks
AI-driven surveillance tools work every time, ranging from data scans to detect red flags or suspicious activities that indicate:
- Security concerns
- Fraudulent actions
- Regulatory violations
- Credential discrepancies
Healthcare Compliance Audit Checklist: Best Practices to Be Included

For example, consider Electronic Health Records (EHRs). AI can monitor login attempts and track suspicious activity, such as unauthorized attempts to access sensitive patient data. When something looks wrong, it can alert hospital staff or the compliance team, who can work to secure data and prevent a HIPAA breach.
Every healthcare organization and provider needs a compliance program that includes communication, education, and a proactive approach. Here is a checklist that helps you ensure you have a reliable foundation for healthcare compliance:
- Execute a Risk Assessment
Learn the key areas of privacy and security risks in your digital healthcare solutions. Review HIPAA, state-specific, and FDA regulations for the healthcare team. Ensure the solution’s overall functionality and design are in line with the standards and regulations, including software development and medical coding compliance.
- Review Policies
Build, distribute, and execute written standards of conduct that define your organization’s dedication to meeting ethical and legal standards. Ensure your policies address core compliance areas, including data security, data privacy, informed consent, and reporting requirements. The standards need to be communicated to every employee, vendor, and contractor that works with your business.
- Analyze Training & Education Programs
Ensure employees have access to frequent education and training programs that cover the latest compliance laws, policies, regulations, and related topics. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the training to ensure that they develop the skills needed to meet healthcare compliance mandates.
- Review Data Security Protocols
Understand your data security protocols, including access controls, encryption, and safe data storage. Ensure these meet industry best practices for healthcare IT compliance.
- Review Incident Response Procedures
Build and maintain open communication so employees can express compliance concerns with zero fear of retaliation, including an anonymous reporting procedure. Follow a process to promptly respond to compliance issues and, to the best of your ability, take corrective disciplinary action for employee non-compliance.
- Regularly Evaluate the Compliance Monitoring
Execute and regularly track internal monitoring, including audits, to measure compliance and promptly resolve known deficiencies.
- Document the Audit
Record the audit findings, which include the areas of non-compliance or possible risks, to analyze the development of action plans to address these concerns.
Healthcare compliance demands ongoing attention and monitoring to ensure the business works within the scope of all applicable standards. By adhering to this compliance audit checklist, you can ensure the organization has an ideal program in place that aligns with its legal and ethical obligations.
Role of NewAgeSysIT in Healthcare Compliance
Healthcare compliance is challenging and involves many phases. It needs strict adherence to many evolving standards while maintaining pace with technological advancements. It requires high-end collaboration to manage investigations, conduct audits, work with third-party vendors, and more.
With the help of a leading healthcare app development company like NewAgeSysIT, you can follow every step of the way with a compliant and hassle-free approach. By offering the best healthcare software development services, we also ensure that the digital solutions comply with healthcare standards and regulations. Our team ensures you establish the best healthcare practices while adhering to global healthcare compliance standards.
If you’re looking for expert advice on healthcare compliance or searching to build healthcare-compliant apps or software, reach out to our healthcare app development experts today!
FAQ
1. What is compliance in healthcare?
Adherence to local, state, or federal health-specific standards is known as healthcare compliance. It aims to minimize fraudulent activities, data breaches, and security risks in the healthcare sector.
2. What are the benefits of healthcare compliance?
Healthcare compliance helps you reduce penalties, data breaches, and healthcare fraud. It also helps you adhere to healthcare policies, protect patient data privacy, minimize financial losses, eliminate complex compliance risks, safeguard your organization’s reputation, and promote a culture of quality healthcare.
3. What is HIPAA compliance in healthcare?
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, otherwise, HIPAA mandates the adoption of industry-wide standards to secure and follow the privacy and confidentiality of patient-specific health data.
4. What are the best software solutions for healthcare compliance management?
Choosing a reputed healthcare software services provider who can guide you through building the most compliant apps and adopt agile development practices to develop healthcare-compliant apps is the best choice you can make. At NewAgeSysIT, we have a team of healthcare app experts to help you create the best healthcare software and applications tailored to meet your goals.
5. How to choose a partner to build healthcare-compliant software?
When choosing a healthcare software development partner, consider whether they have expertise in healthcare software development and a keen focus on security and compliance. Look for a reliable partner like NewAgeSysIT with a strong 30+ year track record, high integration capabilities, strong communication, and a plan for continuous support.
6. How can I ensure compliance with my healthcare apps and software?
Any healthcare app or software that is built with strong security measures, uses innovative technologies, and adheres to regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is compliant. Partnering with a healthcare software development services provider like NewAgeSysIT, which can build software customized to meet your requirements and align with the compliance standards, can help you ensure the solution is super-compliant.




















